What is SRI Index? A Complete Guide
SRI stands for Socially Responsible Investing. The SRI index is designed to constitute a list and rate companies which possess good Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) ratings. Sustainable and responsible investment is becoming increasingly popular. The idea is that ecologically and socially responsible management makes a company sustainable and ensures sustainable returns on investment.
What is the use of SRI Index?
SRI, or investing with a social conscience, is growing in popularity. The premise is that a corporation becomes sustainable and guarantees sustained returns on investment via socially and environmentally responsible management. It is the true form of sustainable and responsible investment.
SRI is a pool of businesses with strong ESG traits for investing. For analyzing stocks and long-term trends identification. It can be used for facilitating the management of the effect on the risk-return profile of the portfolios while monitoring the inclusion of ESG concerns into the investing process. SRI can be used as performance standards and for the assignment of risk and performance. It is a great source of knowledge to create products and do back-testing on various investing methods. Easy risk management by analyzing leaders and performance with simple ratings. A perfect tool for Industry research and analysis. Provides transparency in ESG attributes.
Key Features of SRI Index
The MSCI ESG ratings tend to help investors in targeting their investments towards companies that are concerned about the environmental and social impacts of their policies. Sustainable and responsible investment constitutes of the following features:
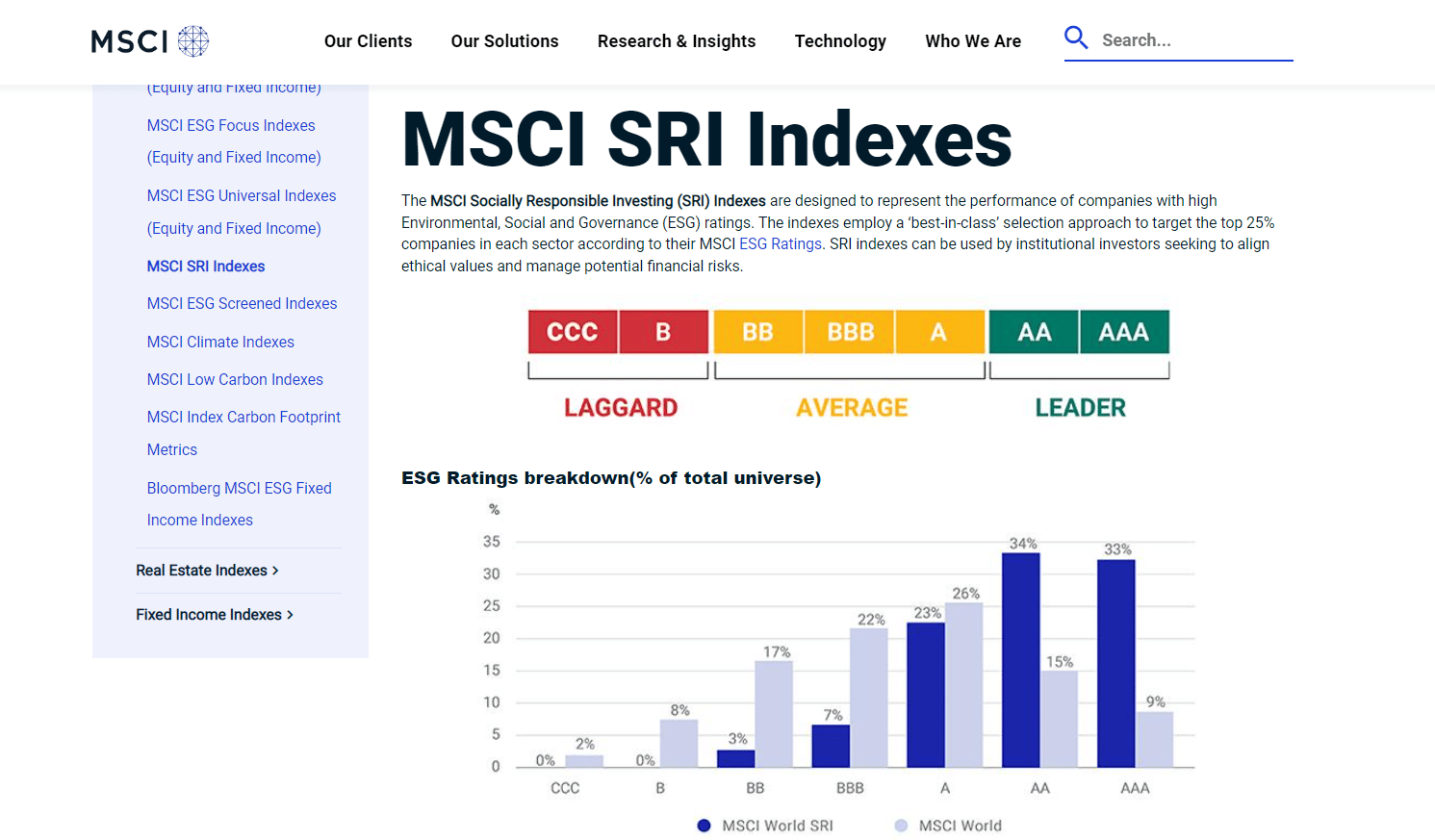
Aims to represent 25% of the market capitalization of each sector. Created with the intention of maintaining regional and sectoral variety and a profile comparable to the parent market cap index Aims to exclude businesses from the list if their goods have adverse social or environmental effects. Designed to reduce the index’s carbon intensity by excluding businesses involved in the mining and production of thermal coal Omit corporations with a history of controversies and embroiled in disputes A security’s weight is determined by its free float market cap. Makes use of data and research like ESG Ratings, ESG Controversies, and Business Involvement research.
Main Components of SRI ESG Index
SRI ESG consists of three primary components which are as follows.
Impact Investing: Instead of just avoiding exposure to activities considered to be socially unwelcome through exclusions, concentrate on investments in enterprises that can accelerate good social change in areas that are relevant to the investor. ESG Integration: Where investors would like to include ESG-related data into their investment process to find businesses that are more adept than their competitors at handling ESG-related risks and opportunities. Values and Constraints: It may aid in balancing an investor’s portfolio with their investing limitations.
What are ESG Scores?
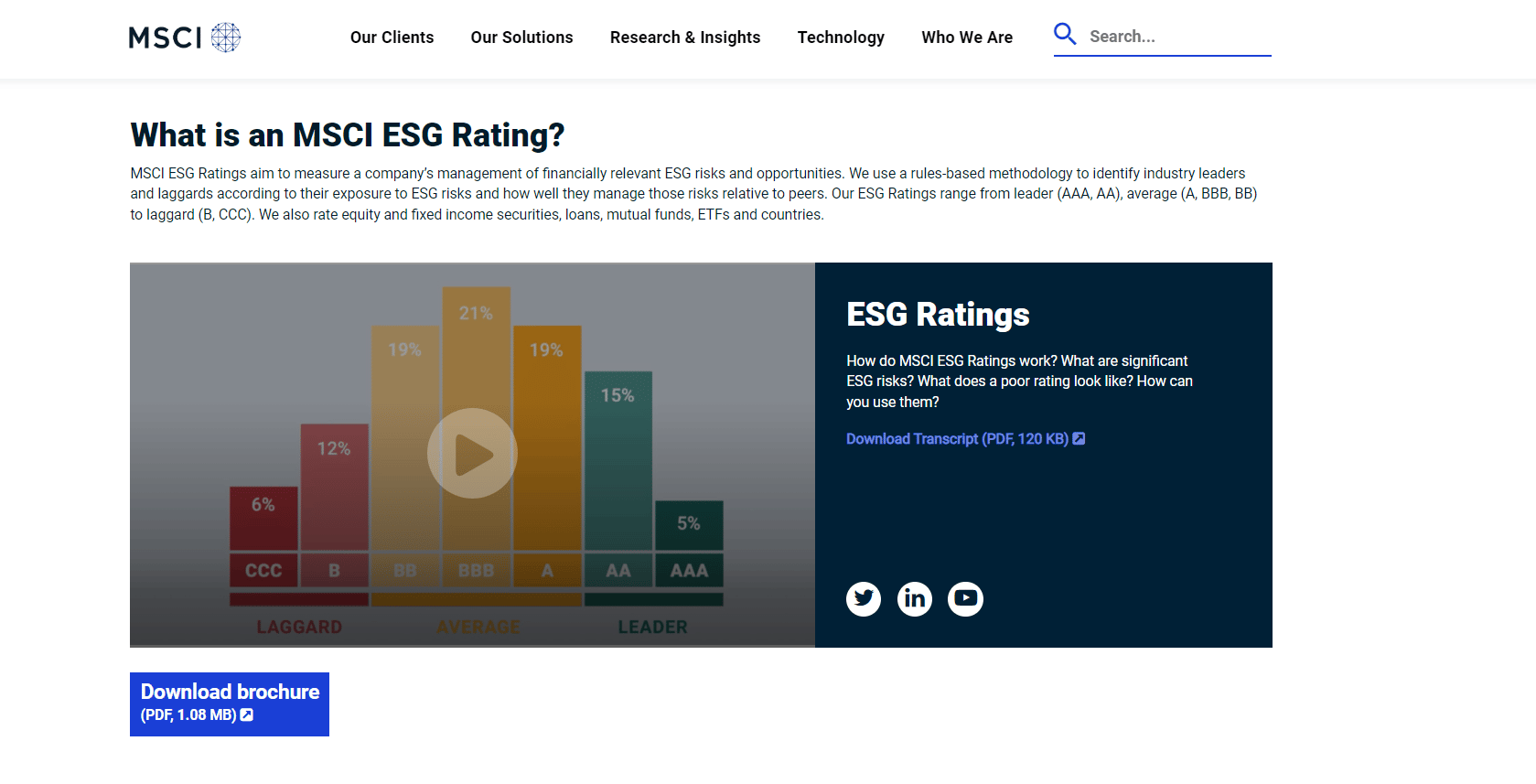
The SRI ESG scores give an evaluation of how exposed organizations are to financial-relevant ESG-related risks and opportunities and how effective their management is at managing such risks and possibilities. These MSCI ESG ratings, which range from CCC to AAA, are translated into these MSCI ESG scores. The meaning of such ratings is as follows:
AAA and AA: A company that excels at addressing the biggest ESG risks and opportunities in its sector comes in one of these categories. A, BBB, and BB: A business that, in comparison to its counterparts in the sector, has a patchy or average track record of handling the biggest ESG risks and opportunities. B and CCC: A business that is behind its competitors in its sector due to high exposure to and poor management of significant ESG risks.
Types of Indexes Under MSCI ESG
Environmental, Social, and Governmental are the three facets on which the indexes are based but every index has some different construction criteria. Some of them are mentioned below.
SRI Index: Top 25% of ESG-rated businesses by free-float market capitalization per GICS sector and Weighted average market capitalization. ESG Leaders: Top 50% of ESG-rated businesses by free-float market capitalization per GICS sector and Weighted average market capitalization. ESG Focus: Improve index-level ESG score within the limitations of tracking error and sector. ESG Universal: Market capitalization weight depends on ESG ratings and ranges from 0.5 to 2.0. ESG Screened: Weighted average market capitalization.
Types of Indexes Under S&P Global ESG
When it comes to S&P Global ESG here are the different types of Indexes in it.
Core ESG: The Dow Jones Sustainability Indexes (DJSI), which targets the top 10% of ESG performances, and the S&P 500 ESG Index, which targets the top 75% of the float market capitalization of each GICS® business group within their parent indices by S&P DJI ESG Score, make up our main ESG indices. ESG Climate: These indexes, which are intended to address climate change and the shift to a low-carbon economy, target various carbon reduction goals, such as carbon-efficient and fossil fuel-free solutions. Thematic ESG: They provide a variety of indexes that give focused exposure to particular ESG issues, such as clean water and energy. Fixed Income ESG: These indexes apply ESG approaches to fixed income strategies and provide access to green bonds, water, and renewable energy.
What is ETF?
An Exchange Traded Index fund or ETF, closely follows the performance of well-known market indices. ETFs are the ideal foundational elements for constructing private financial ventures. ETFs may be exchanged at any time on the stock exchange like shares and simply replicate a market index one-to-one. With only one asset, you may invest profitably in many markets using ETFs. Also Read: Are Teslas Worth it? An Analysis
Use of SRI ETFs
SRI ETFs may be used to invest in a variety of socially conscious indices or SRI ESG. These may have quite different overall approaches, thus not all indexes will be equally suitable to you and your ethical and personal goals. This also creates a crucial area for SRI ETFs and indexes, which normally have a wider scope and stricter selection criteria. These indexes are an excellent fit for investors who have strong moral and environmental values. However, there are several indexes and ETFs available for sustainable investment and they might vary greatly in terms of their aims, methodology, etc. As a result, not every investor will find every sustainable index to be appropriate. We hope you enjoyed learning about SRI Index. Investors, who want to take advantage of the recent rise of investments in eco-friendly and responsible companies, should pay close attention to indices that include subjects like clean energy, water, and electric vehicles for which they can easily make use of the SRI Index. In contrast, institutional investors are particularly interested in climate change ETFs since the underlying indexes are frequently created to satisfy legal obligations for climate protection.